- Tel: +86 813 2105845
- Fax: +86 813 2105845
- Mob: +86 13778532392
- Contact: Mr. Jacky
 info@dinosaurs-world.com
info@dinosaurs-world.com Jackydinosworld@gmail.com
Jackydinosworld@gmail.com Jackyyiming@gmail.com
Jackyyiming@gmail.com Jackyzengdinosaursworld
Jackyzengdinosaursworld
- New species of flying dinosaur discovered in Brazil

Caiuajara dobruskii had a large bony crest on the top of the head that changed from being small and inclined in juveniles to large and steep in adults. Photo: Maurilio Oliveira/Museu Nacional
Evidence of a colony of flying dinosaurs that lived around a desert lake in southern Brazil around 100 million years ago has been uncovered by scientists.
Fossil remains of at least 47 of the previously unknown flying reptiles, with wingspans ranging from two to eight feet (0.65 - 2.35 metres), were discovered at Cruzeiro do Oeste in the southern state of Parana.
Named Caiuajara dobruskii, the pterosaurs are the first to be found so far south in the country, said the study in PLOS ONE.
The huge number of bones could represent hundreds of young and adult individuals, scientists believe.
It is the first time scientists have located a pterosaur "bone bed" containing fossils from many individuals of the same species.The site where they were found covers an area of less than 215 square feet (20 square metres).
Caiuajara dobruskii had a large bony crest on the top of the head that changed from being small and inclined in juveniles to large and steep in adults.
It is thought to have been a gregarious species that learned to fly at a very young age.
Led by Dr Alexander Kellner, from Federal University of Rio de Janeiro, the scientists wrote in the online journal Public Library of Science ONE: "Based on the available information, we conclujde that Caiuajara dobruskii lived in colonies around an inland lake situated in a desert.
"The presence of three main levels of accumulation in a section of less than one metre suggests that this region was home to pterosaur populations for an extended period of time.
"It is also plausible that Caiuajara was a migratory pterosaur that visited this area from time to time, although the first possibility is favoured here.
"The causes of death remain unknown, although similarities with dinosaur drought-related mortality are striking. However, it is also possible that desert storms could have been responsible for the occasional demise of these pterosaurs."
The fossil record of pterosaurs, which lived alongside the dinosaurs but were unrelated to birds, is patchy.
Their bones were fragile and few of the creatures lived in places where fossils form easily, making pterosaur finds rare.
Most have consisted of incomplete skeletons of a single individual.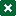

 2014-09-10
2014-09-10
 New dinosaur species help scientists fill in evolutionary gaps
New dinosaur species help scientists fill in evolutionary gaps Feathered everything: just how many dinosaurs had feathers?
Feathered everything: just how many dinosaurs had feathers? Dinosaur Fossil With Fleshy Rooster's Comb Is First of Its Kind
Dinosaur Fossil With Fleshy Rooster's Comb Is First of Its Kind Scientists finally decode how dinosaurs turned into birds and learned how to fly
Scientists finally decode how dinosaurs turned into birds and learned how to fly Dark matter may have killed the dinosaurs, claims scientist
Dark matter may have killed the dinosaurs, claims scientist New duck-billed dinosaur uncovered in Alaska, researchers say
New duck-billed dinosaur uncovered in Alaska, researchers say
- Contact Us
- Tel: +86 813 2105845
- Fax: +86 813 2105845
- Contact: Mr. Jacky
 info@dinosaurs-world.com
info@dinosaurs-world.com Jackydinosworld@gmail.com
Jackydinosworld@gmail.com Jackyyiming@gmail.com
Jackyyiming@gmail.com Jackyzengdinosaursworld
Jackyzengdinosaursworld
- Copyright @ 2009 - 2020 Zigong Dinosaurs World Science & Technology Co.,Ltd.